THE CIVIL CODE LEASE
The majority of our clientele is interested in the civil code lease. We support many companies, foreigners, large groups and embassies. If like them, you are interested in the civil code lease and want to know more, contact us !
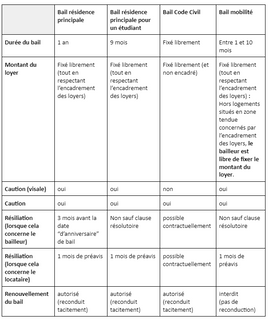
- What is the civil code lease?
In a nutshell, the Civil Code Lease is a type of rental agreement that allows for a secondary residence of the signatory (main tenant). As such, it's comparatively less regulated than a principal residence lease.
This lease is governed by Article 1708 of the Civil Code, which sets that the parties can mutually agree to define three main points: the duration, the conditions of renewal, and the rent. Moreover, Civil Code leases signed for residential use are governed by Law No. 89-462 of July 6, 1989, This is how companies can establish corporate housing for their employees or owners to enjoy a second home.
This type of lease is also used on rental properties considered “atypical” (i.e. properties in rural areas, properties with large spaces, etc.)
2. The risk of non-payment
Even in the context of corporate housing, there's still the risk of unpaid rent. It's either the tenant fails to pay the rent on time, has not paid the rent for a few months now, or even decided to stay on the property beyond the duration of the lease. For the latter, the tenant then becomes a “classic” tenant that will have to adhere to the rules of a principal residence lease. The eviction procedure (in case of unpaid rent) for this is still long but comparatively shorter than as stated in the ALUR Law of 1989.
Unfortunately, unpaid rent insurance from the market does not cover Civil Code Leases. The owner/landlord must ask the tenant for a classic guarantor, whether it is an individual or the company that employs him.
When the lease is signed directly by the company directly, the risk of non-payment is lower. However, it is necessary to remain vigilant and check the profitability and solvency of the company (i.e. by requesting the balance sheets).
3. What is the duration of the civil code lease?
Despite its uncommon nature, A Civil Code Lease is still required to comply with the rules of the law, particularly when it comes to its duration. For this type of lease, the law requires both parties—owner/landlord and tenant—to set the duration in advance. Most importantly, it must not exceed 9 years in total.
For fixed-term Civil Code Leases, the tenant can end the term by simply departing from the property. Or both parties can establish that the lease will automatically renew if there is no objection.
On the other hand, indefinite Civil Code Leases can end the moment one or both parties give their proper notice. But this method still has to respect holiday deadlines and working days as well.
4. What are the owner's obligations?
- Provide the property on the start date of the lease
- Provide a livable property
- Ensure a peaceful atmosphere (i.e. no noise pollution)
- Carry out necessary repairs and renovations
5. What are the tenant's obligations?
- Ensure that the property remains the same throughout the duration of the lease
- Pay rent on time
- Return any stored furniture to its proper place upon the inventory of fixtures
If the tenant fails to fulfill their obligations, the owner/landlord reserves the right to evict the tenant. It's worth noting that the tenant is poorly protected with regard to the eviction procedure in a Civil Code Lease.
6. What are the clauses of the civil code lease?
- A detailed description of the property and equipment
- The use that will be made of the premises (i.e. second home, gatherings of associations, official housing, etc.)
- The price of rent, other rental charges, and their revision procedures
- The agreed duration of the lease
- The terms of assignment and any automatic renewal
- The price of the security deposit
- The obligations of the owner/landlord and tenant
Exclusion from the application of the provisions of the ALUR Law of July 6, 1989.
7. What are the common questions about the civil code lease?
- To what extent are tenants free under this lease?
As long as the tenant respects the conditions of the Civil Code Lease, there are no problems. But there are cases that will allow the landlord to evict the tenant (i.e. unpaid rent).
- Can you get unpaid rent insurance for this lease?
Unfortunately, unpaid rent insurance does not cover Civil Code Leases. You must then ask the tenant for standard guarantor insurance. This applies both to individuals and/or companies that employ them for the company's housing.
- Is this lease more at risk of non-payment?
In the event that a company, business, or organization directly signs a lease under the Civil Code, the risk of non-payment is lower. But it is still worth staying vigilant. Always check the profitability of the lease as well as how it corresponds to the solvency of the company.
To learn more about the mobility lease, click just below ⬇️